-
Unix Words File Download Mac
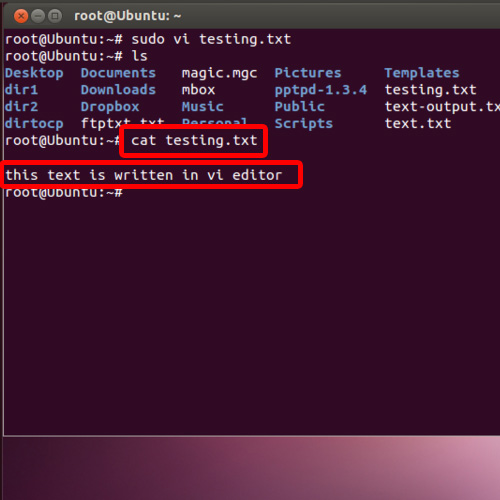
Words is a standard file on Unix and Unix-like operating systems, and is simply a newline-delimited list of dictionary words.It is used, for instance, by spell-checking programs. The words file is usually stored in /usr/share/dict/words or /usr/dict/words. On Debian and Ubuntu, the words file is provided by the wordlist package, or its provider packages wbritish, wamerican, etc. Shell scripts must be executable files in order to run. You can use the chmod command to indicate that the text file is executable (that is, its contents can be run as a shell script). In the Terminal app on your Mac, use the cd command to move into the directory that contains the file you want to make executable.
Terminal User Guide
Shell scripts must be executable files in order to run. You can use the chmod command to indicate that the text file is executable (that is, its contents can be run as a shell script).
-
In the Terminal app on your Mac, use the cd command to move into the directory that contains the file you want to make executable. For example:
-
Enter the chmod command. For example:
% chmod 755 YourScriptName.sh
After making the shell script file executable, you can run it by entering its pathname. For example:
or
% cd ~/Documents/Dev/% ./YourScriptName.shSee alsoAbout shell scripts in Terminal on MacApple Support article: Use zsh as the default shell on your MacScript management with launchd in Terminal on Macchmod command man pagecd command man pageOn Unix-like operating systems, the dos2unix and unix2dos commands convertplain text files from DOS or Mac format to Unix, and vice versa.
Description
In DOS/Windows text files, a line break, also known as newline, is a combination of two characters: a Carriage Return (CR) followed by a Line Feed (LF). In Unix text files a line break is a single character: the Line Feed (LF). In Mac text files, prior to macOS X, a line break was single Carriage Return (CR) character. Nowadays macOS uses Unix style (LF) line breaks.
Binary files are automatically skipped, unless conversion is forced.
Non-regular files, such as directories and FIFOs, are automatically skipped.
Symbolic links and their targets are by default kept untouched. Symbolic links can optionally be replaced, or the output can be written to the symbolic link target. Symbolic links on Windows are not supported. Windows symbolic links are always replaced, keeping the targets unchanged.
Dos2unix was modelled after dos2unix under SunOS/Solaris and has similar conversion modes.
Syntax
Options
--
Treat all options that follow as file names. Use this option, for instance, if you want to convert files whose names start with a dash. So, to convert a file named '-foo', you can use this command:
dos2unix -- -foo Or in new file mode:
dos2unix -n -- -foo out.txt
-ascii
Convert only line breaks. This is the default conversion mode.
-iso
Conversion between DOS and ISO-8859-1 character set. See also section CONVERSION MODES.
-1252
Use Windows code page 1252 (Western European).
-437
Use DOS code page 437 (US). This is the default code page used for ISO conversion.
-850
Use DOS code page 850 (Western European)
-860
Use DOS code page 860 (Portuguese).
-863
Use DOS code page 863 (French Canadian).
-865
Use DOS code page 865 (Nordic).
-7
Convert 8 bit characters to 7 bit space.
-c, --convmodeCONVMODE
Set conversion mode. Where CONVMODE is one of: ascii, 7bit, iso, or mac, with ascii being the default.
-f, --force
Force conversion of binary files.
-h, --help
Display help and exit.
-k, --keepdate
Keep the date stamp of output file same as input file.
-L, --license
Display program's license.
-l, --newline
Add additional newline.
dos2unix: Only DOS line breaks are changed to two Unix line breaks. In Mac mode only Mac line breaks are changed to two Unix line breaks.
unix2dos: Only Unix line breaks are changed to two DOS line breaks. In Mac mode Unix line breaks are changed to two Mac line breaks.
-m, --add-bom
Write an UTF-8 Byte Order Mark in the output file. Never use this option when the output encoding is other than UTF-8. See also section UNICODE.
-n, --newfileINFILE OUTFILE ...
New file mode. Convert file INFILE and write output to file OUTFILE. File names must be given in pairs and wildcard names should not be used or you will lose your files.
The person who starts the conversion in new file (paired) mode will be the owner of the converted file. The read/write permissions of the new file will be the permissions of the original file minus the umask of the person who runs the conversion.
-o, --oldfileFILE ...
Old file mode. Convert file FILE and overwrite output to it. The program defaults to run in this mode. Wildcard names may be used.
In old file (in-place) mode the converted file gets the same owner, group, and read/writepermissions as the original file. Also, when the file is converted by another user who has write permissions on the file (e.g., user root). The conversion will be aborted when it is not possible to preserve the original values. Change of owner could mean that the original owner is not able to read the file any more. Change of group could be a security risk, the file could be made readable for persons for whom it is not intended. Preservation of owner, group, and read/write permissions is only supported on Unix.
-q, --quiet
Quiet mode. Suppress all warnings and messages. The return value is zero. Except when wrong command-line options are used.
-s, --safe
Skip binary files (default).
-F, --follow-symlink
Follow symbolic links and convert the targets.
-R, --replace-symlink
Replace symbolic links with converted files (original target files remain unchanged).
-S, --skip-symlink
Keep symbolic links and targets unchanged (default).
-V, --version
Display version information and exit.
Mac Mode
In normal mode line breaks are converted from DOS to Unix and vice versa. Mac line breaks are not converted.
In Mac mode line breaks are converted from Mac to Unix and vice versa. DOS line breaks are not changed.
To run in Mac mode use the command-line option '-c mac' or use the commands 'mac2unix' or 'unix2mac'.
Conversion Modes

ascii
In mode 'ascii' only line breaks are converted. This is the default conversion mode.
Although the name of this mode is ASCII, which is a 7 bit standard, the actual mode is 8 bit. Use always this mode when converting Unicode UTF-8 files.
7bit
In this mode all 8 bit non-ASCII characters (with values from 128 to 255) are converted to a 7 bit space.
iso
Characters are converted between a DOS character set (code page) and ISO character set ISO-8859-1 (Latin-1) on Unix. DOS characters without ISO-8859-1 equivalent, for which conversion is not possible, are converted to a dot. The same counts for ISO-8859-1 characters without DOS counterpart.
When only option '-iso' is used dos2unix will try to determine the active code page. When this is not possible dos2unix will use default code page CP437, which is mainly used in the USA. To force a specific code page use options '-437' (US), '-850' (Western European), '-860' (Portuguese), '-863' (French Canadian), or '-865' (Nordic). Windows code page CP1252 (Western European) is also supported with option '-1252'. For other code pages use dos2unix in combination with iconv. iconv can convert between a long list of character encodings.
Never use ISO converion on Unicode text files. It will corrupt UTF-8 encoded files.
Some examples:
Convert from DOS default code page to Unix Latin-1:
Convert from DOS CP850 to Unix Latin-1:
Convert from Windows CP1252 to Unix Latin-1:
Convert from Windows CP1252 to Unix UTF-8 (Unicode):
Convert from Unix Latin-1 to DOS default code page:
Convert from Unix Latin-1 to DOS CP850:
Convert from Unix Latin-1 to Windows CP1252:
Convert from Unix UTF-8 (Unicode) to Windows CP1252:
See also http://czyborra.com/charsets/codepages.html and http://czyborra.com/charsets/iso8859.html.
NOTE: Conversion modes ascii, 7bit, and iso are similar to those of dos2unix/unix2dos under SunOS/Solaris.
Unicode
Encodings
There exist different Unicode encodings. On Linux Unicode files are typically encoded in UTF-8 encoding. On Windows Unicode text files can be encoded in UTF-8, UTF-16, or UTF-16 big endian, but are mostly encoded in UTF-16 format.
Conversion
Unicode text files can have DOS, Unix or Mac line breaks, like regular text files.
All versions of dos2unix and unix2dos can convert UTF-8 encoded files, because UTF-8 was designed for backward compatibility with ASCII.
dos2unix and unix2dos with Unicode UTF-16 support can read little and big endian UTF-16 encoded text files. To see if dos2unix was built with UTF-16 support type 'dos2unix -V'.
The Windows versions of dos2unix and unix2dos convert UTF-16 encoded files always to UTF-8 encoded files. Unix versions of dos2unix/unix2dos convert UTF-16 encoded files to the locale character encoding when it is set to UTF-8. Use the locale command to find out what the locale character encoding is.
Because UTF-8 formatted text files are well supported on both Windows and Unix, dos2unix, and unix2dos have no option to write UTF-16 files. All UTF-16 characters can be encoded in UTF-8. Conversion from UTF-16 to UTF-8 is without loss. UTF-16 files will be skipped on Unix when the locale character encoding is not UTF-8, to prevent accidental loss of text. When an UTF-16 to UTF-8 conversion error occurs, for instance when the UTF-16 input file contains an error, the file will be skipped.
ISO and 7-bit mode conversion do not work on UTF-16 files.
Byte Order Mark
On Windows Unicode text files typically have a Byte Order Mark (BOM), because many Windows programs (including Notepad) add BOMs by default. See also https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Byte_order_mark.
On Unix Unicode files typically don't have a BOM. It is assumed that text files are encoded in the locale character encoding.
dos2unix can only detect if a file is in UTF-16 format if the file has a BOM. When an UTF-16 file doesn't have a BOM, dos2unix will see the file as a binary file.
Use dos2unix in combination with iconv to convert an UTF-16 file without BOM.
Dos2unix never writes a BOM in the output file, unless you use option '-m'.
Unix2dos writes a BOM in the output file when the input file has a BOM, or when option '-m' is used.
Examples
Convert from Windows UTF-16 (with BOM) to Unix UTF-8:
Convert from Windows UTF-16 (without BOM) to Unix UTF-8:
Convert from Unix UTF-8 to Windows UTF-8 with BOM:
Convert from Unix UTF-8 to Windows UTF-16:
Recursive Conversion
Use dos2unix in combination with the find and xargs commands to recursively convert text files in a directory tree structure. For instance to convert all .txt files in the directory tree under the current directory type:
Localization
Is Mac Unix Or Linux
LANG

The primary language is selected with the environment variableLANG. The LANG variable consists out of several parts. The first part is in small letters the language code. The second is optional and is the country code in capital letters, preceded with an underscore. There is also an optional third part: character encoding, preceded with a dot. A few examples for POSIX standard type shells:
export LANG=nl
Dutch
export LANG=nl_NL
Dutch, The Netherlands
export LANG=nl_BE
Dutch, Belgium
export LANG=es_ES
Spanish, Spain
export LANG=es_MX
Spanish, Mexico
export LANG=en_US.iso88591
English, USA, Latin-1 encoding
export LANG=en_GB.UTF-8
English, UK, UTF-8 encoding
For a complete list of language and country codes see the gettext manual: https://www.gnu.org/software/gettext/manual/gettext.html#Language-Codes
File Video Download
On Unix systems you can use to command locale to get locale-specific information.
LANGUAGE
With the LANGUAGE environment variable you can specify a priority list of languages, separated by colons. Dos2unix gives preference to LANGUAGE over LANG. For instance, first Dutch and then German: 'LANGUAGE=nl:de'. You have to first enable localization, by setting LANG (or LC_ALL) to a value other than 'C', before you can use a language priority list through the LANGUAGE variable. See also the gettext manual: https://www.gnu.org/software/gettext/manual/gettext.html#The-LANGUAGE-variable
If you select a language that is not available you will get the standard English messages.
DOS2UNIX_LOCALEDIR
With the environment variable DOS2UNIX_LOCALEDIR the LOCALEDIR set during compilation can be overruled. LOCALEDIR is used to find the language files. The GNU default value is '/usr/local/share/locale'. Option --version displays the LOCALEDIR that is used.
Example (POSIX shell):
Return Values
On success, zero is returned. When a system error occurs the last system error will be returned. For other errors 1 is returned.
The return value is always zero in quiet mode, except when wrong command-line options are used.
Examples
Get input from stdin and write output to stdout.
Both of the above commands will do the same thing: convert, and replace, both a.txt and b.txt in one command.
Converts and replaces a.txt while keeping original date stamp.
-

